A control system is a device, or set of devices, that manages, commands, directs or regulates the behavior of other device(s) or system(s). Industrial control systems are used in industrial production. There are two common classes of control systems, with many variations and combinations: logic or sequential controls, and feedback or linear controls. There is also fuzzy logic, which attempts to combine some of the design simplicity of logic with the utility of linear control.
Sunday, June 30, 2013
QUESTION 5
QUESTION 4
QUESTION 3
Temperature control is a process in which change of temperature of a space (and objects collectively there within) is measured or otherwise detected, and the passage of heat energy into or out of the space is adjusted to achieve a desired average temperature.
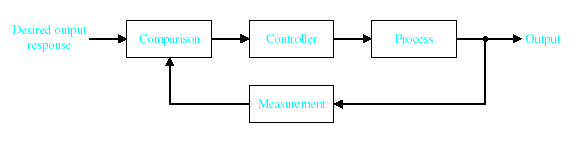
A home thermostat is an example of a closed control loop: It constantly assesses the current room temperature and controls a heater and/or air conditioner to increase or decrease the temperature according to user-defined setting(s). A simple (low-cost, cheap) thermostat merely switches the heater or air conditioner either on or off, and temporary overshoot and undershoot of the desired average temperature must be expected. A more expensive thermostat varies the amount of heat or cooling provided by the heater or cooler, depending on the difference between the required temperature (the "setpoint") and the actual temperature. This minimizes over/undershoot. This method is called Proportional control. Further enhancements using the accumulated error signal (Intergral) and the rate at which the error is changing (Derivative) are used to form more complex PID Controllers which is the form usually seen in industry. 



QUESTION
Pneumatic: A system in which gas pressure differences and their rates of change are related to gas flows, their integrals and their rates of change.
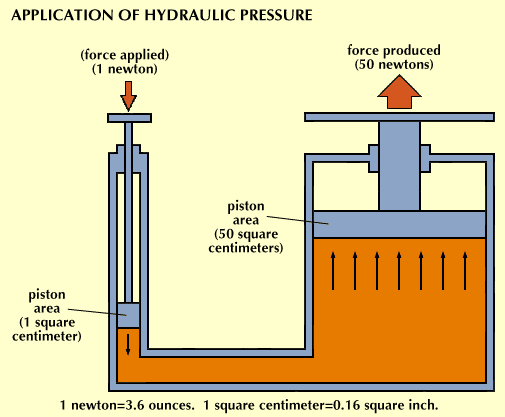
Hydraulic: A mechanism operated by the resistance offered or the pressure transmitted when a liquid is forced through a small opening or tube
System – An interconnection of elements and devices for a desired purpose.
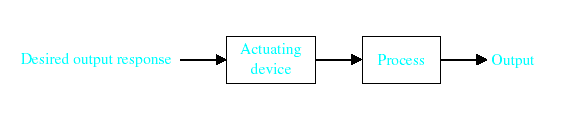
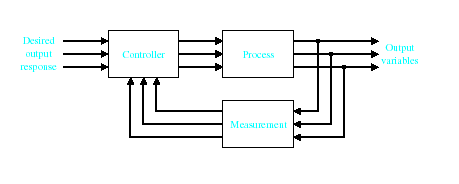
Control System – An interconnection of components forming a system configuration that will provide a desired response.
Process – The device, plant, or system under control. The input and output relationship represents the cause-and-effect relationship of the process.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)


.jpg)
